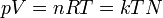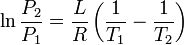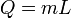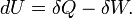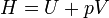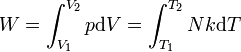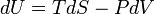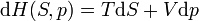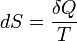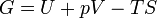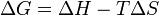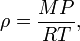Resources on physics related to aerodynamics
The List of elementary physics formulae on wikipedia is useful.
List of variables
| Variable
|
Meaning
|
Unit (SI)
|
| γ (gamma)
|
Surface tension or Heat capacity ratio (adiabatic process in thermodynamics)
|
N.m-1 (Newton per meter)
|
| μ (mu) or η (eta)
|
Viscosity
|
Pa·s (Pascal second) or P (Poise, 1 Poise is 0.1 Pa.s)
|
| ρ (rho)
|
Density
|
kg.m-3 (kg per cubic meter)
|
| C, Cp, CV
|
Heat capacity, general, at constant pressure, at constant volume.
|
J.K-1 (Joule per Kelvin)
|
| G
|
Gibbs free energy
|
J (Joule)
|
| H
|
Enthalpy: total energy of a thermodynamic system.
|
J (Joule)
|
| ΔHvap or L
|
Vaporization heat or Latent heat of vaporization: energy required to vaporize a mole of liquid at a given temperature.
|
J.mol-1 (Joule per mole)
|
| M
|
Mach number
|
no unit
|
| Q
|
Amount of Heat
|
J (Joule)
|
| T
|
Temperature. T0 or Tt is the stagnation temperature.
|
K (Kelvin)
|
| S
|
Entropy
|
J.K-1 (Joule per Kelvin)
|
| U
|
Internal energy of a system (see first law of Thermodynamics below)
|
J (Joule)
|
| V
|
Volume
|
m3 (cubic meter)
|
| W
|
Work: mechanical constraints on the system.
|
J (Joule)
|
| a
|
Speed of sound in medium (used to calculate Mach number)
|
m.s-1
|
| c
|
Velocity of a flow in thermodynamics, also noted V; generally noted u in fluid dynamics.
|
m.s-1
|
| n
|
Quantity of matter
|
mol (mole)
|
| p
|
Pressure. pt is the stagnation pressure.
|
Pa (Pascal)
|
| p
|
Momentum p = m*v, with m the mass and v the velocity, not to be confused with volume.
|
kg.m.s-1
|
List of constants
List of equations
| Equation
|
Name
|
Meaning
|
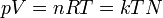
|
Ideal gas equation
|
Relation between properties of an ideal gas (state equation). k is kB.
|
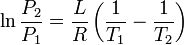
|
Clausius-Clapeyron relation
|
Relation between the pressure, latent heat of vaporization and temperature of a vapour at two temperatures (approximation, at low temperatures).
|
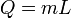
|
Heat at state change for an ideal gas.
|
The heat required to change the state of a some matter, L being the latent heat. Delta H equals Q only when pressure is constant (isobaric).
|
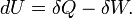
|
First law of thermodynamics
|
Variations of internal energy of a system between two states is the sum of the received heat and work (minus the given work).
|
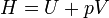
|
Enthalpy
|
Total amount of energy of a system, defined as the sum of the internal energy U of the system and pressure * volume at the boundary of the system and its environment.
|
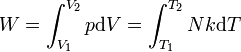
|
Work of gas expansion.
|
Work done by expanding an ideal gas.
|
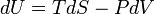
|
Internal energy change related to entropy
|
Internal energy related to entropy variation for a closed system in thermal equilibrium (fundamental thermodynamic relation).
|
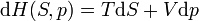
|
Enthalpy change
|
Enthalpy change depending on entropy and pressure changes, equation created from the mix of the basic ones above.
|
| ΔSuniverse = ΔSsurroundings + ΔSsystem
|
Entropy variation as a whole.
|
Entropy variation of a system is generally compensated by the inverse variation of the surroundings, not including losses.
|
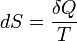
|
Second law of thermodynamics
|
A change in the entropy of a system is the infinitesimal transfer of heat to a closed system driving a reversible process, divided by the equilibrium temperature of the system.
|
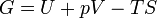
|
Gibbs free energy / Free enthalpy
|
Useful work obtainable from a system at isobaric and isothermal conditions. Since H is U + pV, it can be replaced in the equation, making G = H - TS.
|
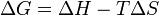
|
Gibbs free energy variation.
|
If ΔG < 0, the system's transformation can be spontaneous, if ΔG = 0 the transformation is inversible and the system is in an equilibrium state, if ΔG > 0 it can't be spontaneous.
|
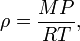
|
Density of an ideal gas.
|
M is molar mass. This means that the density of an ideal gas can be doubled by doubling the pressure, or by halving the absolute temperature.
|