Aero formulas: Difference between revisions
From NPrize
Jump to navigationJump to search
→List of variables: enthalpy link |
Heat equations |
||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
=Resources on physics related to aerodynamics= | =Resources on physics related to aerodynamics= | ||
The [ | The [https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/List_of_elementary_physics_formulae List of elementary physics formulae] on wikipedia is useful. | ||
==List of variables== | ==List of variables== | ||
| Line 25: | Line 25: | ||
| [https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Vaporization_heat Vaporization heat] or [https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Latent_heat Latent heat of vaporization]: energy required to vaporize a mole of liquid at a given temperature. | | [https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Vaporization_heat Vaporization heat] or [https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Latent_heat Latent heat of vaporization]: energy required to vaporize a mole of liquid at a given temperature. | ||
| J.mol<sup>-1</sup> (Joule per mole) | | J.mol<sup>-1</sup> (Joule per mole) | ||
|- | |||
| Q | |||
| Amount of [https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Heat Heat] | |||
| J (Joule) | |||
|- | |- | ||
| T | | T | ||
| Line 81: | Line 85: | ||
|[https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Clausius%E2%80%93Clapeyron_relation#Ideal_gas_approximation_at_low_temperatures Clausius-Clapeyron relation] | |[https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Clausius%E2%80%93Clapeyron_relation#Ideal_gas_approximation_at_low_temperatures Clausius-Clapeyron relation] | ||
|Relation between the pressure, latent heat of vaporization and temperature of a vapour at two temperatures (approximation, at low temperatures). | |Relation between the pressure, latent heat of vaporization and temperature of a vapour at two temperatures (approximation, at low temperatures). | ||
|- | |||
|style="background:white"| {{SERVER}}/images/formulas_mirror/Qdefinition.png | |||
|Definition of [https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Heat#Path-independent_examples_for_an_ideal_gas Heat] for an ideal gas. | |||
|The heat required to change the temperature of a system from an initial temperature T<sub>0</sub>, to a final temperature, T<sub>f</sub>. | |||
|- | |||
|style="background:white"| {{SERVER}}/images/formulas_mirror/QeqmL.png | |||
|Heat at [https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Latent_heat#Specific_latent_heat state change] for an ideal gas. | |||
|The heat required to change the state of a some matter, L being the latent heat. | |||
|- | |||
|} | |} | ||
Revision as of 01:09, 29 March 2012
The List of elementary physics formulae on wikipedia is useful.
List of variables
| Variable | Meaning | Unit (SI) |
|---|---|---|
| γ (gamma) | Surface tension | N.m-1 (Newton per meter) |
| μ (mu) or η (eta) | Viscosity | Pa·s (Pascal second) or P (Poise, 1 Poise is 0.1 Pa.s) |
| H | Enthalpy: energy of a thermodynamic system. | J (Joule) |
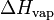 or L or L
|
Vaporization heat or Latent heat of vaporization: energy required to vaporize a mole of liquid at a given temperature. | J.mol-1 (Joule per mole) |
| Q | Amount of Heat | J (Joule) |
| T | Temperature | K (Kelvin) |
| V | Volume | m3 (cubic meter) |
| n | Quantity of matter | mol (mole) |
| p | Pressure | Pa (Pascal) |
List of constants
| Constant | Meaning | Value | Unit (SI) |
|---|---|---|---|
| NA or N | Avogadro constant, number of atoms or molecules in a mole. | 6.02214129.1023 | mol-1 |
| R | ideal gas constant | 8.3144621 | J.K−1.mol−1 |
| kB or k | Boltzmann constant, gas constant R divided by Avogadro number. | 1.3806488.10-23 | J.K-1 |
List of equations
| Equation | Name | Meaning |
|---|---|---|
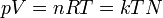
|
Ideal gas equation | Relation between properties of an ideal gas (state equation). k is kB. |
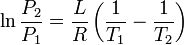
|
Clausius-Clapeyron relation | Relation between the pressure, latent heat of vaporization and temperature of a vapour at two temperatures (approximation, at low temperatures). |

|
Definition of Heat for an ideal gas. | The heat required to change the temperature of a system from an initial temperature T0, to a final temperature, Tf. |
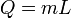
|
Heat at state change for an ideal gas. | The heat required to change the state of a some matter, L being the latent heat. |